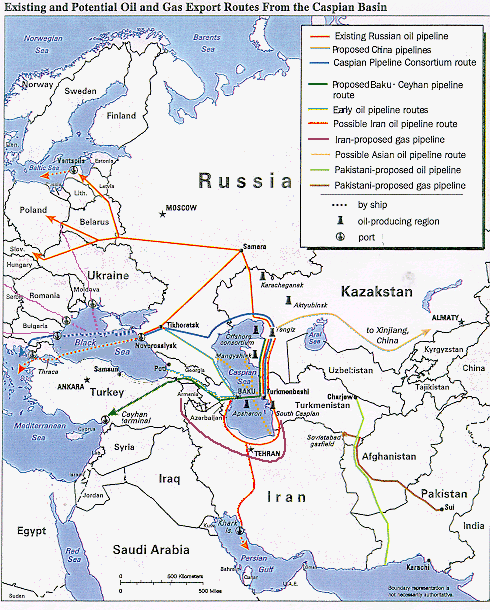
 The
Caspian Sea area has
proven oil reserves of fifteen to twenty-eight billion barrels plus
estimated reserves of 40-178 billion, a total of 206 billion
barrels--16 percent of the earth's potential oil reserves (compared to
Saudi's 261 billion barrels of oil and America's own 22 billion
barrels). Even at today's low prices, that could add up to $3 trillion
in oil. With the Saudi regime tottering--an aging king about to die,
widespread internal corruption creating calls for revolutionary
overthrow--and a new source of oil and gas in the Caucasus, the
Standard Oil suzerainty is looking to create a new regime in Saudi
Arabia and develop a new center of operations in Southern Asia.
The
Caspian Sea area has
proven oil reserves of fifteen to twenty-eight billion barrels plus
estimated reserves of 40-178 billion, a total of 206 billion
barrels--16 percent of the earth's potential oil reserves (compared to
Saudi's 261 billion barrels of oil and America's own 22 billion
barrels). Even at today's low prices, that could add up to $3 trillion
in oil. With the Saudi regime tottering--an aging king about to die,
widespread internal corruption creating calls for revolutionary
overthrow--and a new source of oil and gas in the Caucasus, the
Standard Oil suzerainty is looking to create a new regime in Saudi
Arabia and develop a new center of operations in Southern Asia.The huge oil and gas reserves in the Caspian Sea must either be moved west to European markets or south to Asian markets. The western route is to move oil from Chechnya, across the Black Sea and through the Bosporus to the Mediterranean, but the narrow Bosporus channel is already clogged with oil tankers from the Black Sea oilfields. An alternate route would be to move the tankers from the Black Sea, bypassing the Bosporus, up the Danube River and then through a very short pipeline across Kosovo to the Mediterranean at Tirana, Albania. However, that process was stopped by the Chinese who have supplied and armed the Albanians, as a client state, since 1949.
The other difficulty with the western route is that Western Europe is a tough market, characterized by high prices for oil products, an aging population, and increasing competition from natural gas. Furthermore, the region is fiercely competitive, now being serviced by oil from the Middle East, the North Sea, Scandinavia, and Russia. Western Europe is not a very attractive market, because substantial infrastructure would have to be developed to bring that oil from the Caspian to an already overly-competitive European market.
The only other ways to get Caspian Sea oil and gas to Asian markets is through China, which is too long a route, or through Iran, which is politically and economically inimical to U.S.-Standard Oil objectives.
As soon as the Soviets discovered the vast Caspian Sea oilfields in the late 1970's, they attempted to take control of Afghanistan to
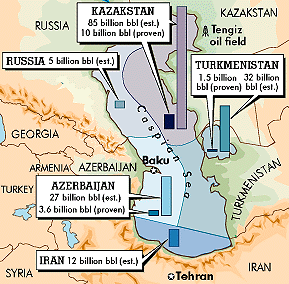 build a massive north-south
pipeline system to allow the Soviets to send their oil directly through
Afghanistan and Pakistan to the Indian Ocean seaport. The result was
the decades long Soviet-Afghan war. The Standard Oil-influenced U.S.
government saw the danger of a Russian north-south pipeline and the CIA
trained and funded armed terrorist groups, including Osama bin Laden,
who defeated the Soviets in the late 1980's.
build a massive north-south
pipeline system to allow the Soviets to send their oil directly through
Afghanistan and Pakistan to the Indian Ocean seaport. The result was
the decades long Soviet-Afghan war. The Standard Oil-influenced U.S.
government saw the danger of a Russian north-south pipeline and the CIA
trained and funded armed terrorist groups, including Osama bin Laden,
who defeated the Soviets in the late 1980's.The Russians then tried to control the flow of oil and gas through its monopoly on pipelines. The Southern Asian Republics of the former Soviet Union--Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan--saw through this Russian monopolistic ploy and began to consult with Western companies.
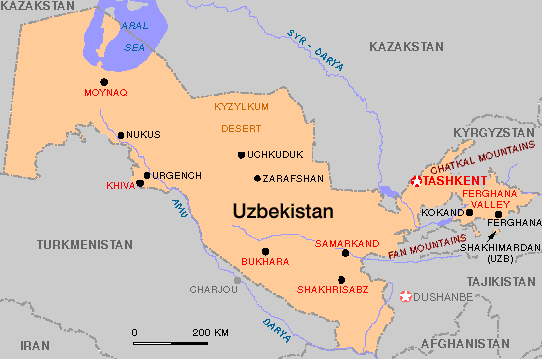 The
Standard Oil-influenced
U.S. government now plans to thrust further along the 40th parallel
from the Balkans through these Southern Asian Republics of the former
Soviet Union. The U.S. military has already set up a permanent
operations base in Uzbekistan. The so-called anti-terrorist strategy is
clearly designed to simultaneously consolidate control over Middle
Eastern and South Asian oil, and contain and neutralize the former
Soviet Union. With that strategy, Afghanistan is exactly where they
need to be.
The
Standard Oil-influenced
U.S. government now plans to thrust further along the 40th parallel
from the Balkans through these Southern Asian Republics of the former
Soviet Union. The U.S. military has already set up a permanent
operations base in Uzbekistan. The so-called anti-terrorist strategy is
clearly designed to simultaneously consolidate control over Middle
Eastern and South Asian oil, and contain and neutralize the former
Soviet Union. With that strategy, Afghanistan is exactly where they
need to be.Russia, realizing its weaker position vis-a-vis the United States, has been making noises as if it fully agreed with the U.S. incursions in Afghanistan. But Russia has joined the Shangahi Cooperation Organization (SCO) which includes China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Takijistan and Uzbekistan. China is using the SCO to try to align Russia economically and politically towards China and northeast Asia. Russia's membership in the SCO is an attempt to maintain its traditional hegemony in Central Asia. The underlying rationale of the SCO is the control of its members' enormous reserves of oil and gas.
Despite the misgivings of Russia, China, India, or any other nation, Afghanistan will now become the base of operations in
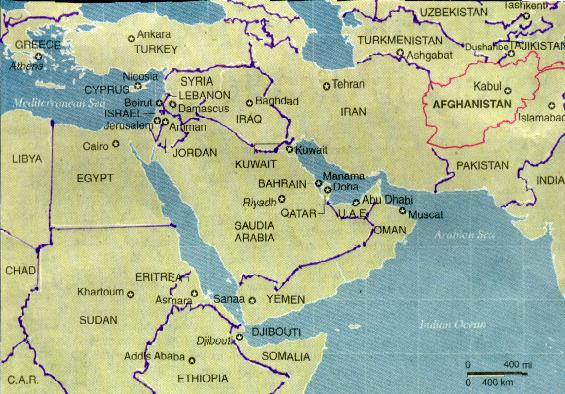 destabilizing, isolating, and establishing
control over the South Asian Republics and the Middle-East. After the
conquest of this area is complete and the permanent military posts are
set up, they will begin construction of a pipeline through
Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan to deliver petroleum to the
Asian market.
destabilizing, isolating, and establishing
control over the South Asian Republics and the Middle-East. After the
conquest of this area is complete and the permanent military posts are
set up, they will begin construction of a pipeline through
Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan to deliver petroleum to the
Asian market. UNOCAL,
the spearhead for
Standard Oil interests, has been trying to build the north-south
pipeline through Afghanistan and Pakistan to the Indian Ocean for
several decades. In 1998, the California-based UNOCAL, which held 46.5
percent stakes in Central Asia Gas (CentGas), a consortium that planned
an ambitious gas pipeline across Afghanistan, withdrew in frustration
after several fruitless years. The pipeline was to stretch 1,271 km
from Turkmenistan's Dauletabad fields to Multan in Pakistan at an
estimated cost of $1.9 billion. An additional $600 million would have
brought the pipeline to energy-hungry India.
UNOCAL,
the spearhead for
Standard Oil interests, has been trying to build the north-south
pipeline through Afghanistan and Pakistan to the Indian Ocean for
several decades. In 1998, the California-based UNOCAL, which held 46.5
percent stakes in Central Asia Gas (CentGas), a consortium that planned
an ambitious gas pipeline across Afghanistan, withdrew in frustration
after several fruitless years. The pipeline was to stretch 1,271 km
from Turkmenistan's Dauletabad fields to Multan in Pakistan at an
estimated cost of $1.9 billion. An additional $600 million would have
brought the pipeline to energy-hungry India.In the spring of 2001, Halliburton, Vice President Dick Cheney's company, signed a major contract with the State Oil Company of Azerbaijan to develop a 6000-square-meter marine base to support offshore oil construction in the Caspian Sea. The base will be used to assist Halliburton's catamaran crane vessel, the Qurban Abbasov, in upcoming offshore pipe-laying and subsea activities, according to a statement the company released May 15, 2001.
 UNOCAL
cut off its earlier
agreement with the Taliban in 1998 when it became clear that the
Taliban could not control all of Afghanistan and provide a stable
political environment for a north-south pipeline construction project.
It was likely at this juncture that a new "war against terrorism" ploy
was conceived by the Standard Oil-influenced U.S. government. The "war
against terrorism" in Afghanistan has come to a hiatus, with war-lords
once again ruling the country, and the Bush administration has put
their own man, Karzai, in power to control Afghanistan.
UNOCAL
cut off its earlier
agreement with the Taliban in 1998 when it became clear that the
Taliban could not control all of Afghanistan and provide a stable
political environment for a north-south pipeline construction project.
It was likely at this juncture that a new "war against terrorism" ploy
was conceived by the Standard Oil-influenced U.S. government. The "war
against terrorism" in Afghanistan has come to a hiatus, with war-lords
once again ruling the country, and the Bush administration has put
their own man, Karzai, in power to control Afghanistan.Karzai was a top adviser to UNOCAL during the negotiations with the Taliban to
 construct a Central
Asia Gas (CentGas) pipeline from Turkmenistan through western
Afghanistan to Pakistan. Karzai is the leader of the southern Afghan
Pashtun Durrani tribe. A member of the mujaheddin that fought the
Soviets during the 1980s, Karzai was a top contact for the CIA,
maintaining close relations with CIA Director William Casey, Vice
President George Bush, and their Pakistani Inter Service Intelligence
(ISI) Service go-between. After the Soviet Union left Afghanistan, the
CIA sponsored the relocation of Karzai and a number of his brothers to
the U.S.
construct a Central
Asia Gas (CentGas) pipeline from Turkmenistan through western
Afghanistan to Pakistan. Karzai is the leader of the southern Afghan
Pashtun Durrani tribe. A member of the mujaheddin that fought the
Soviets during the 1980s, Karzai was a top contact for the CIA,
maintaining close relations with CIA Director William Casey, Vice
President George Bush, and their Pakistani Inter Service Intelligence
(ISI) Service go-between. After the Soviet Union left Afghanistan, the
CIA sponsored the relocation of Karzai and a number of his brothers to
the U.S.The real motives for the Bush administration's war in Afghanistan are clear for all to see. The U.S. Ambassador to Pakistan, Wendy Chamberlain, met with Pakistan's oil minister, Usman Aminuddin, in January, 2002 to continue plans for the north-south pipeline, encouraging the construction of Pakistan's Arabian Sea oil terminus for the pipeline.
President Bush says our military will continue its presence in Afghanistan, which means that while the U.N. forces serve as a paramilitary police force, U.S. soldiers will be guarding the construction of the north-south pipeline.
 To
assure that the pipeline project will proceed apace, the
Afghani-American Zalmay Khalilzad, a previous member of the CentGas
project, became President Bush's Special National Security Assistant.
Khalilzad has recently been named presidential Special Envoy for
Afghanistan. Khalilzad is a Pashtun and the son of a former government
official under King Mohammed Zahir Shah. Along with being a consultant
to the RAND Corporation, he was a special liaison between UNOCAL and
the Taliban government. Khalilzad also worked on various risk analyses
for the project under the direction of National Security Advisor
Condoleezza Rice, a former member of the board of Chevron.
To
assure that the pipeline project will proceed apace, the
Afghani-American Zalmay Khalilzad, a previous member of the CentGas
project, became President Bush's Special National Security Assistant.
Khalilzad has recently been named presidential Special Envoy for
Afghanistan. Khalilzad is a Pashtun and the son of a former government
official under King Mohammed Zahir Shah. Along with being a consultant
to the RAND Corporation, he was a special liaison between UNOCAL and
the Taliban government. Khalilzad also worked on various risk analyses
for the project under the direction of National Security Advisor
Condoleezza Rice, a former member of the board of Chevron.